Here are two different ways to do it. We can define functions - #bold-table() and #no-stroke-table() that are wrappers for table.
You can also style tables without wrapping them in functions and marking them by labels instead. The same label can be applied to one or more tables.
The two tables in the example look like this:
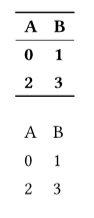
These are prototypes - first implement the styles you want
#let headers = ([A], [B])
#let data = range(4).map(str)
#let hrule = table.hline(stroke: 0.08em)
#{
show table: set text(weight: "bold")
table(
columns: 2,
stroke: (x, y) => if y == 0 { (top: 0.08em, bottom: 0.04em) } else { none },
table.header(..headers),
..data,
hrule
)
}
#table(
columns: 2,
stroke: none,
table.header(..headers),
..data,
)
---
Finished versions: using functions - translate the style into functions
#let bold-table(..args) = {
show table: set text(weight: "bold")
table(
stroke: (x, y) => if y == 0 { (top: 0.08em, bottom: 0.04em) } else { none },
..args
)
}
#let no-stroke-table = table.with(stroke: none)
#bold-table(
columns: 2,
table.header(..headers),
..data,
hrule
)
#no-stroke-table(
columns: 2,
table.header(..headers),
..data
)
---
Finished versions - using labels to set style
#show <bold-table>: set text(weight: "bold")
#show <bold-table>: set table(stroke: (x, y) => if y == 0 { (top: 0.08em, bottom: 0.04em) } else { none })
#show <no-stroke-table>: set table(stroke: none)
#table(
columns: 2,
table.header(..headers),
..data,
hrule
)<bold-table>
#table(
columns: 2,
table.header(..headers),
..data
)<no-stroke-table>