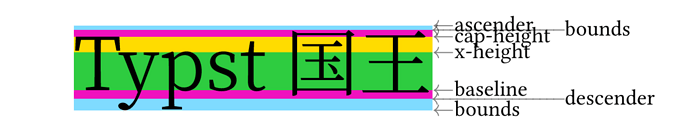
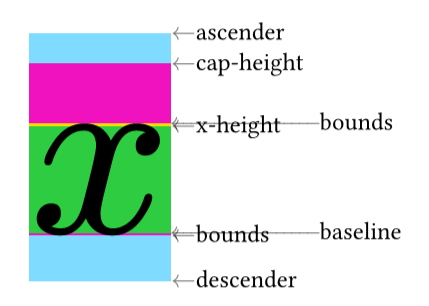
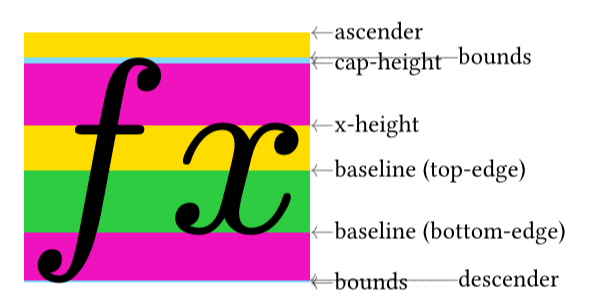
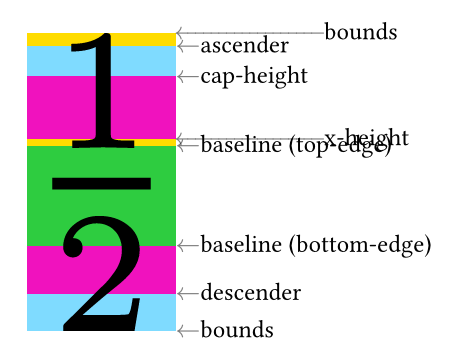
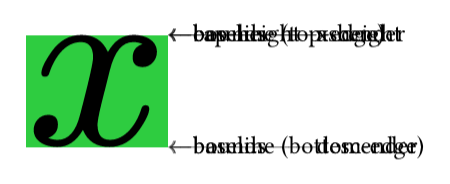
Here is a snippet to debug font by visualize baseline, x-height, cap-height, descender, ascender, and bounds.
It might be helpful if you meet issues on baseline alignment between mixed scripts.
Example usage
#import "debug-font.typ": debug-font
#set page(height: auto, width: auto, margin: (left: 1em, right: 3.5em, y: 0.5em))
#debug-font({
set text(font: "Source Han Serif")
[Typst 国王]
})
Source of the above example
This text will be hidden
#set page(height: auto, width: auto, margin: 0.5em)
#set text(fallback: false, lang: "en", font: ("Libertinus Serif", "Source Han Serif"))
#show heading: set text(1.2em)
#show heading: pad.with(bottom: 0.25em)
#let debug-font-big(body) = debug-font({
set text(2em)
body
})
= Libertinus Serif (default)
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Libertinus Serif")
[“Typst”,.:!? αβωΩ uüUÜ]
})
= New Computer Modern
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Libertinus Serif")
[“Typst”,.:!? αβωΩ uüUÜ]
})
= Source Han Serif / Noto Serif CJK / 思源宋体
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Source Han Serif")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
= SimSun / 中易宋体
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "SimSun")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
There are many versions of SimSun, and the above is the one \ included with Windows.
However, some old crazy versions \ set ascender = cap-height = x-height.
= Source Han Sans / Noto Sans CJK / 思源黑体
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Source Han Sans")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
= SimHei / 中易黑体
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "SimHei")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
= FangSong / 中易仿宋
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "FangSong")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
= Kaiti / 中易楷体
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Kaiti")
[Typst,.:!“国王《永》”,。:!]
})
= Notes
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Libertinus Serif")
[u]
})
#h(2em)
#debug-font-big({
set text(font: "Libertinus Serif")
[gÜ]
})
Bounds may vary with the specific text.
Relevant docs
#set text(top-edge: …, bottom-edge: …)
#set par(leading: …, spacing: …)
Definition of debug-font
/// Visualize the conceptual frame around an example text.
///
/// https://typst.app/docs/reference/text/text/#parameters-top-edge
/// https://typst.app/docs/reference/text/text/#parameters-bottom-edge
/// https://forum.typst.app/t/a-snippet-to-debug-font-by-visualize-baseline-cap-height-etc/4597/
#let debug-font(
models: (
(top-edge: "bounds"),
(top-edge: "ascender"),
(top-edge: "cap-height"),
(top-edge: "x-height"),
(top-edge: "baseline"),
(bottom-edge: "descender"),
(bottom-edge: "bounds"),
),
palette: (aqua, fuchsia, green, yellow, fuchsia, aqua),
example-body,
) = {
assert(models.len() - 1 == palette.len())
context {
// Measure heights and sort increasingly
let edge-heights = models
.map(raw-m => {
// Fill with defaults
let m = (top-edge: "baseline", bottom-edge: "baseline", ..raw-m)
// Measure the height of the example
let h = measure(text(..m, example-body)).height
// Calculate the sign of the height
if m.top-edge != "baseline" and m.bottom-edge == "baseline" {
(m.top-edge, h)
} else if m.top-edge == "baseline" and m.bottom-edge != "baseline" {
(m.bottom-edge, -h)
} else {
assert(m.top-edge == m.bottom-edge and m.bottom-edge == "baseline")
assert(h == 0pt)
(m.top-edge, h)
}
})
.sorted(key: ((e, h)) => h)
// Make sure `place(bottom, dy: …)` is relative to the baseline
set text(bottom-edge: "baseline")
box({
// Draw stripes
let heights = edge-heights.map(((e, h)) => h)
for (h-low, h-high, fill) in heights.slice(0, -1).zip(heights.slice(1), palette) {
place(bottom, dy: -h-low, box(height: h-high - h-low, fill: fill, hide(example-body)))
}
// Write the example
example-body
})
// Write annotations
box({
let last-h = none
let long-arrow = false
for (edge, h) in edge-heights {
// if too narrow, change the arrow size
if last-h != none and calc.abs(h - last-h) < 0.2em.to-absolute() {
long-arrow = not long-arrow
} else {
long-arrow = false
}
let arrow-size = if long-arrow { 6em } else { 1em }
place(
bottom,
dy: -h + 0.3em / 2,
text(
0.3em,
bottom-edge: "descender",
text(black.transparentize(50%), $stretch(arrow.l, size: #arrow-size)$) + edge,
),
)
last-h = h
}
})
}
}