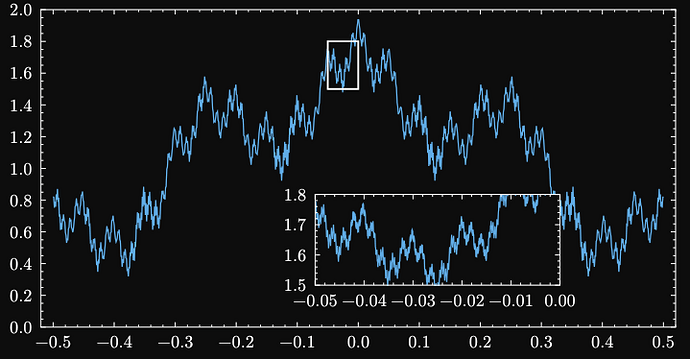
Hi. Lilaq has something like this, but it’s more of an emulation:
#import "@preview/lilaq:0.2.0" as lq
#let weierstrass(x, k: 8) = {
range(k).map(k => calc.pow(0.5, k) * calc.cos(calc.pow(5, k) * x)).sum()
}
#let xs = lq.linspace(-0.5, .5, num: 1000)
#let xs-fine = lq.linspace(-0.05, 0, num: 1000)
#show: lq.set-grid(stroke: none)
#lq.diagram(
width: 14cm,
height: 7cm,
ylim: (0, 2),
margin: (x: 2%),
lq.plot(xs, mark: none, xs.map(weierstrass)),
lq.rect(-0.05, 1.5, width: .05, height: .3),
lq.place(
60%,
100% - 1.2em,
align: bottom,
lq.diagram(
width: 5.4cm,
height: 2cm,
margin: 0%,
ylim: (1.5, 1.8),
fill: white,
lq.plot(xs-fine, mark: none, xs-fine.map(weierstrass)),
),
),
)
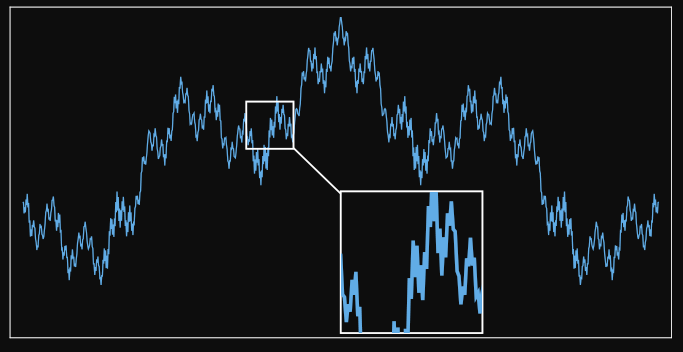
So we can apply the same concept with CeTZ:
#import "@preview/cetz:0.3.4"
#let unit = 1cm
// Magnify content.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - size (array): size of the area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify(scale, place-pos, pos, size, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line
rect(pos, (rel: (size.first(), -1 * size.last())), name: "a")
content(
anchor: "north-west",
name: "b",
place-pos,
block(
stroke: 1pt,
width: size.first() * unit * scale,
height: size.last() * unit * scale,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(dx: -pos.first() * unit, dy: pos.last() * unit, body),
),
),
)
line("a", "b")
}
And then get:
Full example
#import "@preview/cetz:0.3.4"
#import "@preview/lilaq:0.2.0" as lq
#let unit = 1cm
#let canvas = cetz.canvas.with(length: unit)
#let weierstrass(x, k: 8) = {
range(k).map(k => calc.pow(0.5, k) * calc.cos(calc.pow(5, k) * x)).sum()
}
#let xs = lq.linspace(-0.5, .5, num: 1000)
#let xs-fine = lq.linspace(-0.05, 0, num: 1000)
#show: lq.set-grid(stroke: none)
#let image = box(
lq.diagram(
width: 14cm,
height: 7cm,
ylim: (0, 2),
margin: (x: 2%),
yaxis: (ticks: none),
xaxis: (ticks: none),
lq.plot(xs, mark: none, xs.map(weierstrass)),
),
)
// Magnify content.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - size (array): size of the area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify(scale, place-pos, pos, size, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line
rect(pos, (rel: (size.first(), -1 * size.last())), name: "a")
content(
anchor: "north-west",
name: "b",
place-pos,
block(
stroke: 1pt,
width: size.first() * unit * scale,
height: size.last() * unit * scale,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(dx: -pos.first() * unit, dy: pos.last() * unit, body),
),
),
)
line("a", "b")
}
#canvas({
import cetz.draw: *
content((0, 0), anchor: "north-west", image)
magnify(300%, (7, -3.9), (5, -2), (1, 1), image)
})
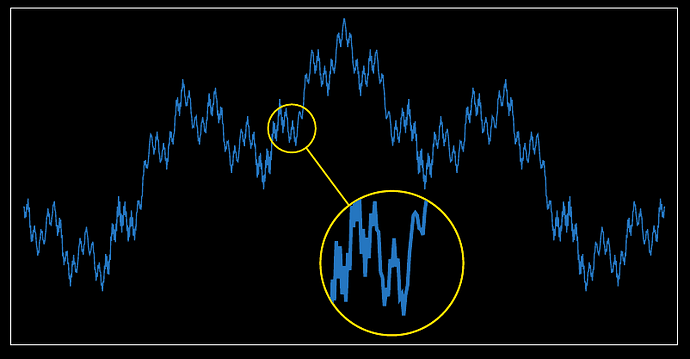
There are plenty of other variations of this, but most of them are more complicated, for example, if you want to connect all 4 corners with 4 lines, or use another shape, etc.
Here is the yellow circle:
// Magnify content.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - diameter (int, float): size of the area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify(scale, place-pos, pos, diameter, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line, circle, set-style
let color = yellow
set-style(stroke: color)
circle(pos, radius: diameter / 2 * unit, name: "a")
circle(place-pos, radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit, name: "b")
line("a", "b")
content(
(),
block(
stroke: 1pt + color,
radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit,
width: diameter * scale * unit,
height: diameter * scale * unit,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(
dx: (-pos.first() + diameter / 2) * unit,
dy: (pos.last() + diameter / 2) * unit,
body,
),
),
),
)
}
Full example
#import "@preview/cetz:0.3.4"
#import "@preview/lilaq:0.2.0" as lq
#let unit = 1cm
#let canvas = cetz.canvas.with(length: unit)
#let weierstrass(x, k: 8) = {
range(k).map(k => calc.pow(0.5, k) * calc.cos(calc.pow(5, k) * x)).sum()
}
#let xs = lq.linspace(-0.5, .5, num: 1000)
#let xs-fine = lq.linspace(-0.05, 0, num: 1000)
#show: lq.set-grid(stroke: none)
#let image = box(
lq.diagram(
width: 14cm,
height: 7cm,
ylim: (0, 2),
margin: (x: 2%),
yaxis: (ticks: none),
xaxis: (ticks: none),
lq.plot(xs, mark: none, xs.map(weierstrass)),
),
)
// Magnify content.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - diameter (int, float): size of the area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify(scale, place-pos, pos, diameter, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line, circle, set-style
let color = yellow
set-style(stroke: color)
circle(pos, radius: diameter / 2 * unit, name: "a")
circle(place-pos, radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit, name: "b")
line("a", "b")
content(
(),
block(
stroke: 1pt + color,
radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit,
width: diameter * scale * unit,
height: diameter * scale * unit,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(
dx: (-pos.first() + diameter / 2) * unit,
dy: (pos.last() + diameter / 2) * unit,
body,
),
),
),
)
}
#canvas({
import cetz.draw: *
content((0, 0), anchor: "north-west", image)
magnify(300%, (8, -5.3), (5.9, -2.5), 1, image)
})
Should work with raster images, but I haven’t tested that.
Looks like it works perfectly well with images, but you do have to lock both axis, otherwise it will scale incorrectly. For this, you can do
#let image = {
let image = image.with("file.png")
context image(..measure(image(width: 20cm)))
}
Raster image
Image link
#import "@preview/cetz:0.3.4"
#let unit = 1cm
#let canvas = cetz.canvas.with(length: unit)
// Magnify content using circle.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - diameter (int, float): size of the circle area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify-circle(scale, place-pos, pos, diameter, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line, circle, set-style
let color = yellow
set-style(stroke: color)
circle(pos, radius: diameter / 2 * unit, name: "a")
circle(place-pos, radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit, name: "b")
line("a", "b")
content(
(),
block(
stroke: 1pt + color,
radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit,
width: diameter * scale * unit,
height: diameter * scale * unit,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(
dx: (-pos.first() + diameter / 2) * unit,
dy: (pos.last() + diameter / 2) * unit,
body,
),
),
),
)
}
// Magnify content using rectangle.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - size (array): size of the rectangle area to magnify
// - body (content): what to magnify
#let magnify-rect(scale, place-pos, pos, size, body) = {
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line
rect(pos, (rel: (size.first(), -1 * size.last())), name: "a")
content(
anchor: "north-west",
name: "b",
place-pos,
block(
stroke: 1pt,
width: size.first() * unit * scale,
height: size.last() * unit * scale,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(dx: -pos.first() * unit, dy: pos.last() * unit, body),
),
),
)
line("a", "b")
}
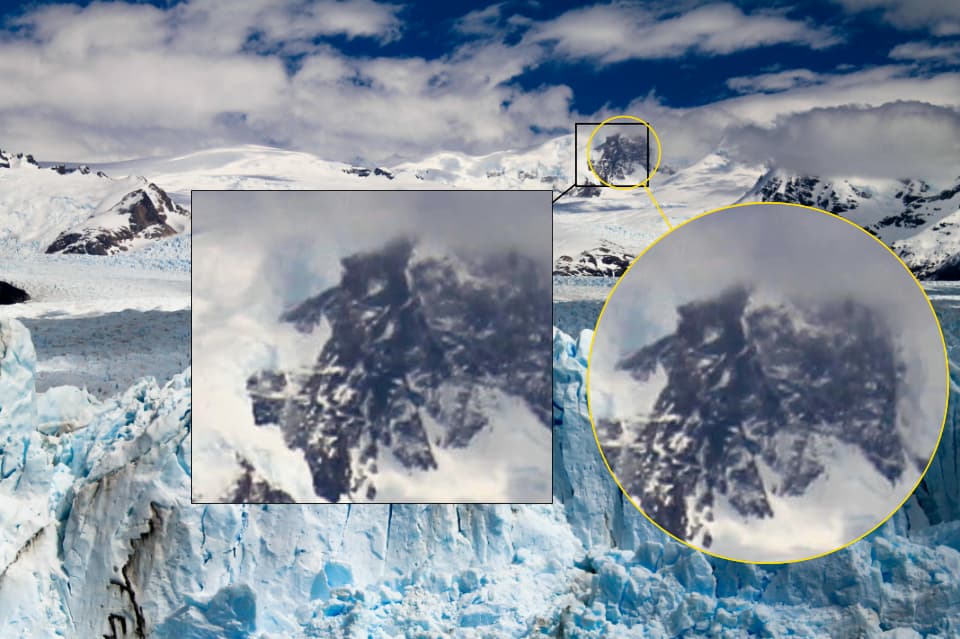
#let image = {
let image = image.with("glacier.jpg")
context image(..measure(image(width: 20cm)))
}
#set page(width: auto, height: auto, margin: 0pt)
#canvas({
import cetz.draw: *
content((0, 0), anchor: "north-west", image)
magnify-rect(500%, (4, -4), (12, -2.6), (1.5, 1.3), image)
magnify-circle(500%, (16, -8), (13, -3.2), 1.5, image)
})
Or, if you want to just edit image, without needing for canvas:
code
#import "@preview/cetz:0.3.4"
// Magnify content using circle.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - body (content): what to magnify
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - diameter (int, float): size of the area to magnify
// - unit (length): unit to use to convert int/float numbers
// - color (length): stroke color
#let magnify-circle(
scale,
body,
place-pos: (0, 0),
pos: (0, 0),
diameter: 1,
unit: 1cm,
color: yellow,
) = {
let canvas = cetz.canvas.with(length: unit)
canvas({
import cetz.draw: content, line, circle, set-style
content((0, 0), anchor: "north-west", body)
set-style(stroke: color)
circle(pos, radius: diameter / 2 * unit, name: "a")
circle(place-pos, radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit, name: "b")
line("a", "b")
content(
(),
block(
stroke: 1pt + color,
radius: diameter / 2 * scale * unit,
width: diameter * scale * unit,
height: diameter * scale * unit,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(
dx: (-pos.first() + diameter / 2) * unit,
dy: (pos.last() + diameter / 2) * unit,
body,
),
),
),
)
})
}
// Magnify content using rectangle.
//
// - scale (ratio): magnification scale
// - body (content): what to magnify
// - place-pos (array): position of the magnification
// - pos (array): where in the content to magnify
// - size (array): size of the area to magnify
// - unit (length): unit to use to convert int/float numbers
#let magnify-rect(
scale,
body,
place-pos: (0, 0),
pos: (0, 0),
size: (1, 1),
unit: 1cm,
) = {
let canvas = cetz.canvas.with(length: unit)
canvas({
import cetz.draw: content, rect, line
content((0, 0), anchor: "north-west", body)
rect(pos, (rel: (size.first(), -1 * size.last())), name: "a")
content(
anchor: "north-west",
name: "b",
place-pos,
block(
stroke: 1pt,
width: size.first() * unit * scale,
height: size.last() * unit * scale,
clip: true,
std.scale(
scale,
reflow: true,
move(dx: -pos.first() * unit, dy: pos.last() * unit, body),
),
),
)
line("a", "b")
})
}
#set page(width: auto, height: auto, margin: 0pt)
#let image = {
let image = image.with("glacier.jpg")
context image(..measure(image(width: 20cm)))
}
#magnify-circle(
500%,
image,
place-pos: (16, -8),
pos: (13, -3.2),
diameter: 1.5,
)
#magnify-rect(
500%,
image,
place-pos: (4, -4),
pos: (12, -2.6),
size: (1.5, 1.3),
)